forked from platypush/platypush
parent
cd2b0a2666
commit
27ee490264
1 changed files with 323 additions and 234 deletions
557
README.md
557
README.md
|
|
@ -32,13 +32,6 @@
|
||||||
* [Complex hook conditions](#complex-hook-conditions)
|
* [Complex hook conditions](#complex-hook-conditions)
|
||||||
* [Turn off the lights at 1 AM](#turn-off-the-lights-at-1-am)
|
* [Turn off the lights at 1 AM](#turn-off-the-lights-at-1-am)
|
||||||
* [Greet me with lights and music when I come home](#greet-me-with-lights-and-music-when-i-come-home)
|
* [Greet me with lights and music when I come home](#greet-me-with-lights-and-music-when-i-come-home)
|
||||||
- [HTTP API](#http-api)
|
|
||||||
* [The _Execute_ tab](#the-_execute_-tab)
|
|
||||||
- [Websocket API](#websocket-api)
|
|
||||||
* [Events](#events)
|
|
||||||
* [Actions](#actions)
|
|
||||||
- [Web hooks](#web-hooks)
|
|
||||||
- [Entities](#entities)
|
|
||||||
- [Core Installation](#core-installation)
|
- [Core Installation](#core-installation)
|
||||||
* [System package manager installation](#system-package-manager-installation)
|
* [System package manager installation](#system-package-manager-installation)
|
||||||
+ [Arch Linux](#arch-linux)
|
+ [Arch Linux](#arch-linux)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -46,13 +39,23 @@
|
||||||
+ [Fedora](#fedora)
|
+ [Fedora](#fedora)
|
||||||
* [`pip`](#pip)
|
* [`pip`](#pip)
|
||||||
* [Docker](#docker)
|
* [Docker](#docker)
|
||||||
|
+ [Base image installation](#base-image-installation)
|
||||||
|
+ [The docker-compose way](#the-docker-compose-way)
|
||||||
|
+ [Exposing host devices](#exposing-host-devices)
|
||||||
* [Manual installation](#manual-installation)
|
* [Manual installation](#manual-installation)
|
||||||
- [Plugins installation](#plugins-installation)
|
- [Plugins installation](#plugins-installation)
|
||||||
* [`pip`](#pip-1)
|
* [`pip`](#pip-1)
|
||||||
* [Web interface](#web-interface)
|
* [Web interface](#web-interface)
|
||||||
* [Docker](#docker-1)
|
* [Docker (`platydock`)](#docker-platydock)
|
||||||
* [Virtual environment](#virtual-environment)
|
* [Virtual environment (`platyvenv`)](#virtual-environment-platyvenv)
|
||||||
* [Manual installation](#manual-installation-1)
|
* [Manual installation](#manual-installation-1)
|
||||||
|
- [HTTP API](#http-api)
|
||||||
|
* [The _Execute_ tab](#the-_execute_-tab)
|
||||||
|
- [Websocket API](#websocket-api)
|
||||||
|
* [Events](#events)
|
||||||
|
* [Actions](#actions)
|
||||||
|
- [Web hooks](#web-hooks)
|
||||||
|
- [Entities](#entities)
|
||||||
- [Configuration](#configuration)
|
- [Configuration](#configuration)
|
||||||
* [Configuration file](#configuration-file)
|
* [Configuration file](#configuration-file)
|
||||||
+ [Scripts directory](#scripts-directory)
|
+ [Scripts directory](#scripts-directory)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -539,7 +542,317 @@ procedure.some_other_procedure:
|
||||||
- action: procedure.at_home
|
- action: procedure.at_home
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Or using the API (see next section).
|
Or using the [available APIs](#http-api).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Core Installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### System package manager installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Arch Linux
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You can either install the
|
||||||
|
[`platypush`](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/platypush) package (for the
|
||||||
|
latest stable version) or the
|
||||||
|
[`platypush-git`](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/platypush-git) package
|
||||||
|
(for the latest git version) through your favourite AUR package manager. For
|
||||||
|
example, using `yay`:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
$ yay platypush
|
||||||
|
# Or
|
||||||
|
$ yay platypush-git
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The Arch Linux packages on AUR are automatically updated upon new git commits
|
||||||
|
or tags.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Debian/Ubuntu
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. Add the Platypush APT key to your trusted keyring:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# wget -q -O \
|
||||||
|
/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/platypush.asc \
|
||||||
|
https://apt.platypush.tech/pubkey.txt
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
2. Add the Platypush repository to your APT sources:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# wget -q -O \
|
||||||
|
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/platypush.list \
|
||||||
|
https://apt.platypush.tech/lists/platypush-<deb_version>-<branch>.list
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Where:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- `deb_version` can be either:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- `stable`: current Debian stable
|
||||||
|
- `oldstable`: previous Debian stable
|
||||||
|
- `ubuntu`: latest Ubuntu release
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- `branch` can be either:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- `main`: latest stable release
|
||||||
|
- `dev`: a package always in sync with the latest git version
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For example, to install the latest stable tags on Debian stable:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# wget -q -O \
|
||||||
|
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/platypush.list \
|
||||||
|
https://apt.platypush.tech/lists/platypush-stable-main.list
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
3. Update your repos and install Platypush:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# apt update
|
||||||
|
# apt install platypush
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Fedora
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RPM builds targeting the latest Fedora release are automatically built on every
|
||||||
|
push pipeline.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To install Platypush via RPM on Fedora:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- Add the Platypush RPM repository configuration to the package manager:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# yum config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.platypush.tech/platypush.repo
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- Install Platypush, either the latest stable release or the rolling release
|
||||||
|
updated on every commit to the main branch:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# yum install platypush
|
||||||
|
# Or
|
||||||
|
# yum install platypush-git
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### `pip`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
$ pip install platypush
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Or, for the latest git version:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
# Official repo
|
||||||
|
$ pip install git+https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush
|
||||||
|
# Github mirror
|
||||||
|
$ pip install git+https://github.com/blacklight/platypush
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Docker
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Base image installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
$ docker run -it --name platypush \
|
||||||
|
-p 8008:8008 \
|
||||||
|
-e "PLATYPUSH_DEVICE_ID=my-device"
|
||||||
|
-v /path/to/your/platypush/config:/etc/platypush \
|
||||||
|
-v /path/to/your/platypush/share:/var/lib/platypush \
|
||||||
|
quay.io/platypush/platypush
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The Web service will be available on `http://localhost:8008`, and a default
|
||||||
|
configuration file will be initialized under
|
||||||
|
`/path/to/your/platypush/config/config.yaml` if not available. The next
|
||||||
|
executions of the service can be triggered via `docker start platypush`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Note that this will install an Alpine-based image. For other base images (e.g.
|
||||||
|
Debian, Ubuntu or Fedora) please consult the [custom docker-compose
|
||||||
|
way](#the-docker-compose-way).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Also note that any extra plugin dependencies installed in the container will be
|
||||||
|
lost if the container is removed.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In order to preserve the state of the container after installing and configuring
|
||||||
|
your plugins, you can leverage the `docker commit` command:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
❯ docker ps
|
||||||
|
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
|
||||||
|
f00546d3bd35 quay.io/platypush/platypush "/bin/sh -c 'platypu…" 38 minutes ago Up 8 minutes 0.0.0.0:8008->8008/tcp, :::8008->8008/tcp platypush
|
||||||
|
❯ docker commit f00546d3bd35 my-custom-platypush-image
|
||||||
|
sha256:13d4a4cae4e7eedee924a8a79deae9a9978aa70b46699c1f2abfd16bf5ed910b
|
||||||
|
# You can now use the my-custom-platypush-image even if the container is destroyed
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Alternatively, you can use [the `platydock` command](#docker-(platydock)) to
|
||||||
|
directly create a Docker image or a `Dockerfile` from a configuration, with all
|
||||||
|
the required plugins and dependencies pre-installed.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### The docker-compose way
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
$ git clone https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush.git
|
||||||
|
$ cd platypush
|
||||||
|
# Copy .env.example to .env and edit docker-compose.yml if required.
|
||||||
|
# In particular, you may want /etc/platypush and /var/lib/platypush
|
||||||
|
# to point to directories on your hosts
|
||||||
|
$ docker compose up
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Note that the default `Dockerfile` uses Alpine, but in `docker-compose.yml` you
|
||||||
|
can also specify an alternative `Dockerfile` - Debian, Ubuntu and Fedora are
|
||||||
|
supported.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Exposing host devices
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Note that some plugins may require access to the host hardware - such as USB
|
||||||
|
devices, Bluetooth adapters etc.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In order to make these devices visible to the Docker container you may need to
|
||||||
|
explicitly mount them as volumes.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For example, the [`serial`
|
||||||
|
plugin](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/serial.html) may need to
|
||||||
|
access an Arduino/ESP device over USB. You can export only that device to the
|
||||||
|
Docker container:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
$ docker run --device=/dev/ttyUSB0 ...
|
||||||
|
# Or, if you set up static naming via udev rules
|
||||||
|
$ docker run --device=/dev/arduino ...
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Or, through `docker-compose.yml`:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```yaml
|
||||||
|
services:
|
||||||
|
platypush:
|
||||||
|
# ...
|
||||||
|
devices:
|
||||||
|
- /dev/ttyUSB0
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Otherwise, for privileged access to the USB bus on a Linux host:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
$ docker run --priviliged -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb ...
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Or, through `docker-compose.yml`:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```yaml
|
||||||
|
services:
|
||||||
|
platypush:
|
||||||
|
# ...
|
||||||
|
volumes:
|
||||||
|
- /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Manual installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
$ git clone https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush.git
|
||||||
|
$ cd platypush
|
||||||
|
$ pip install .
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Plugins installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
All the plugins included in the main repo will be available once you have
|
||||||
|
installed the core platform.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
However, some plugins may require extra (optional) dependencies. You have
|
||||||
|
several ways of installing those dependencies:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### `pip`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You can install extra dependencies via pip extras:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
pip install 'platypush[plugin1,plugin2,...]'
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
pip install 'platypush[light.hue,music.mpd,rss]'
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Will install Platypush with the dependencies for the `light.hue`, `music.mpd`
|
||||||
|
and `rss` plugins.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Web interface
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
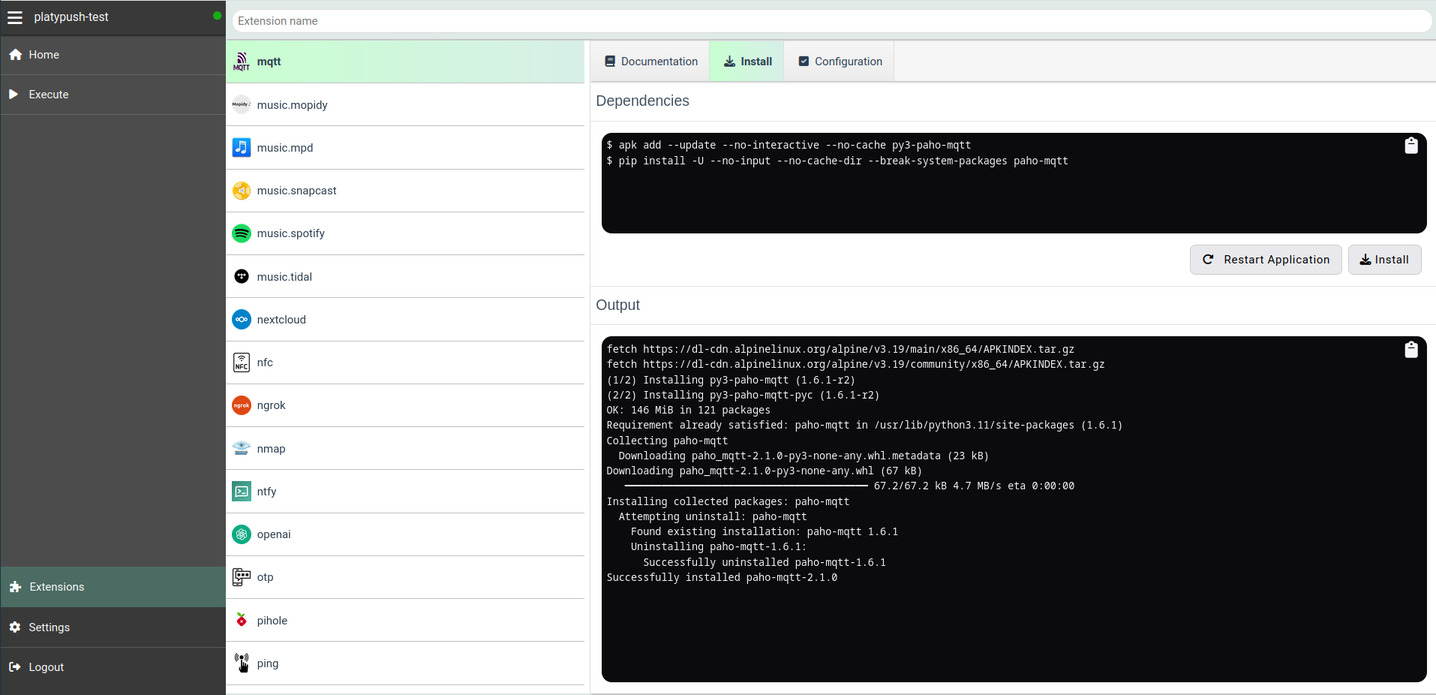
Plugins can be installed from the Web interface too. Navigate to the
|
||||||
|
_Extensions_ entry in the sidebar, select the extension that you want to install,
|
||||||
|
select the _Install_ tab and click _Install_.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
This section also includes the _Configuration_ tab, with a ready-to-paste
|
||||||
|
configuration snippet template for that plugin, as well as a documentation page
|
||||||
|
that includes all the actions supported by a given plugin and the events it
|
||||||
|
triggers.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Docker (`platydock`)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If you already have the base installation of Platypush on your machine, and you
|
||||||
|
have a configuration file with a custom set of integrations, then you may opt
|
||||||
|
to generate a custom Docker image from your configuration file, with all the
|
||||||
|
extra dependencies configured, using the `platydock` command.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The following command:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```shell
|
||||||
|
❯ platydock -c /path/to/your/config.yaml -d platypush-test
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Will create a Platypush Docker image for a device with ID `platypush-test`,
|
||||||
|
with all the requirements for the additional integrations listed in
|
||||||
|
`config.yaml`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You can pass the `--print` option if you just want to print the content of the
|
||||||
|
output `Dockerfile` instead of generating the image.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
By default the image will use Alpine Linux as a base. You can use the
|
||||||
|
`-i`/`--image` to specify another supported base image - `ubuntu`, `debian` or
|
||||||
|
`fedora`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Virtual environment (`platyvenv`)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If you already have the base installation of Platypush on your machine, and you
|
||||||
|
have a configuration file with a custom set of integrations, then you may opt
|
||||||
|
to generate a custom virtual environment from your configuration file, with all
|
||||||
|
the extra dependencies configured, using the `platyvenv` command.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The following command:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
❯ platyvenv -c /path/to/your/config.yaml -o /path/to/your/venv
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Will create a new virtual environment under `/path/to/your/venv` using the
|
||||||
|
specified `config.yaml` to determine which optional dependencies should be installed.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You can then run Platypush after activating your new environment:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
❯ source /path/to/your/venv/bin/activate
|
||||||
|
❯ platypush -c /path/to/your/config.yaml
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Manual installation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The [plugin/backend documentation](https://docs.platypush.tech) reports all the
|
||||||
|
dependencies required by each plugin, as well as the commands to install them
|
||||||
|
on multiple platforms.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If you want to customize your installation, or if you need to install
|
||||||
|
dependencies for a plugin that requires some manual steps, you can check out
|
||||||
|
any plugin-specific installation steps from its documentation.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## HTTP API
|
## HTTP API
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -773,230 +1086,6 @@ the home panel of the Web UI.
|
||||||
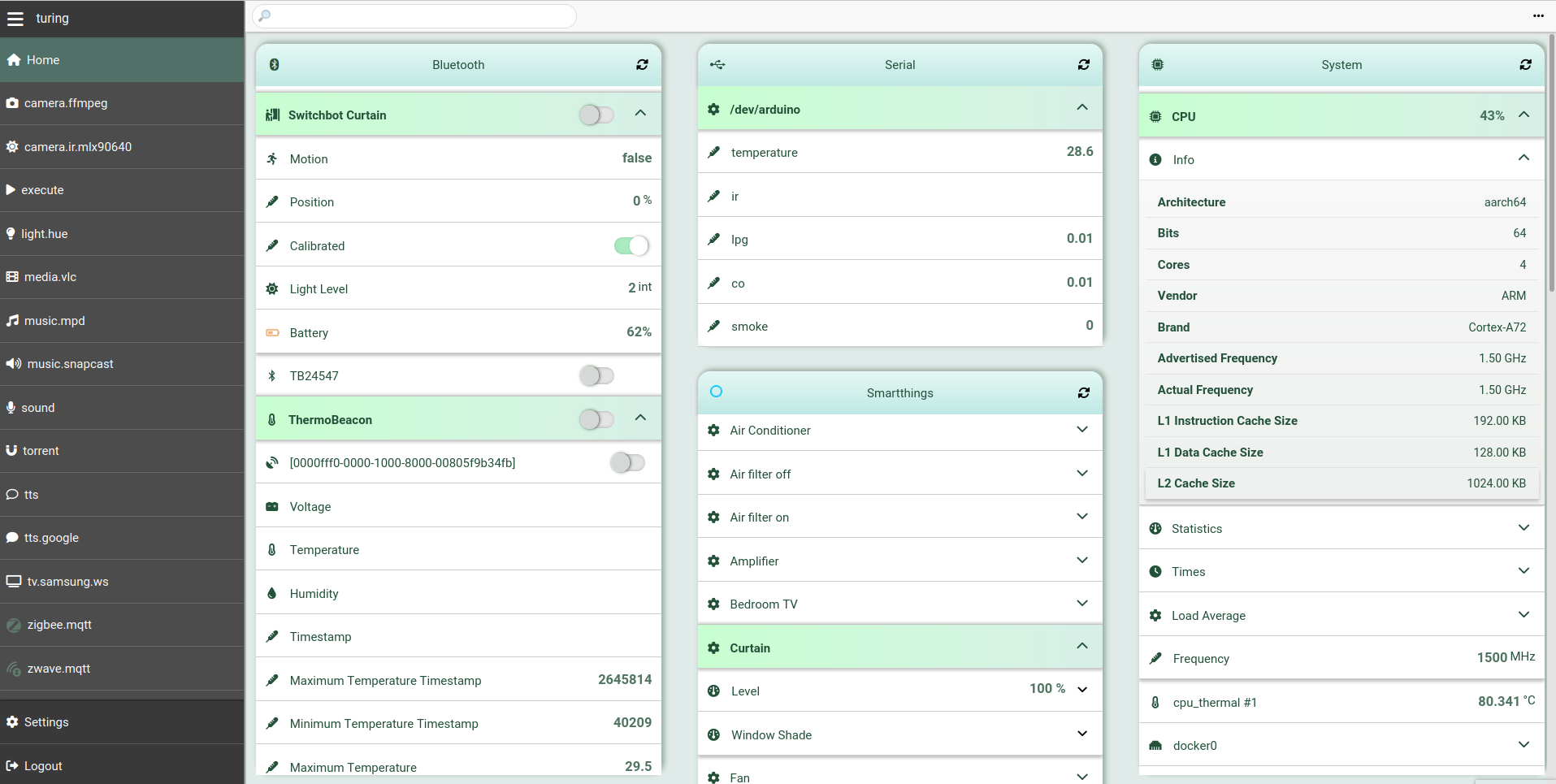
|
panel, showing the Bluetooth, Serial, SmartThings and System integrations](https://platypush-static.s3.nl-ams.scw.cloud/screenshots/main-panel-screenshot-1.png)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Core Installation
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### System package manager installation
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Arch Linux
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You can either install the
|
|
||||||
[`platypush`](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/platypush) package (for the
|
|
||||||
latest stable version) or the
|
|
||||||
[`platypush-git`](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/platypush-git) package
|
|
||||||
(for the latest git version) through your favourite AUR package manager. For
|
|
||||||
example, using `yay`:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
|
||||||
$ yay platypush
|
|
||||||
# Or
|
|
||||||
$ yay platypush-git
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The Arch Linux packages on AUR are automatically updated upon new git commits
|
|
||||||
or tags.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Debian/Ubuntu
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
1. Add the Platypush APT key to your trusted keyring:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# wget -q -O \
|
|
||||||
/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/platypush.asc \
|
|
||||||
https://apt.platypush.tech/pubkey.txt
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
2. Add the Platypush repository to your APT sources:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# wget -q -O \
|
|
||||||
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/platypush.list \
|
|
||||||
https://apt.platypush.tech/lists/platypush-<deb_version>-<branch>.list
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Where:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- `deb_version` can be either:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- `stable`: current Debian stable
|
|
||||||
- `oldstable`: previous Debian stable
|
|
||||||
- `ubuntu`: latest Ubuntu release
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- `branch` can be either:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- `main`: latest stable release
|
|
||||||
- `dev`: a package always in sync with the latest git version
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For example, to install the latest stable tags on Debian stable:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# wget -q -O \
|
|
||||||
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/platypush.list \
|
|
||||||
https://apt.platypush.tech/lists/platypush-stable-main.list
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
3. Update your repos and install Platypush:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# apt update
|
|
||||||
# apt install platypush
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Fedora
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
RPM builds targeting the latest Fedora release are automatically built on every
|
|
||||||
push pipeline.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To install Platypush via RPM on Fedora:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- Add the Platypush RPM repository configuration to the package manager:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# yum config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.platypush.tech/platypush.repo
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- Install Platypush, either the latest stable release or the rolling release
|
|
||||||
updated on every commit to the main branch:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
# yum install platypush
|
|
||||||
# Or
|
|
||||||
# yum install platypush-git
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### `pip`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
|
||||||
$ pip install platypush
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Or, for the latest git version:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
|
||||||
# Official repo
|
|
||||||
$ pip install git+https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush
|
|
||||||
# Github mirror
|
|
||||||
$ pip install git+https://github.com/blacklight/platypush
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Docker
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
|
||||||
$ git clone https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush.git
|
|
||||||
$ cd platypush
|
|
||||||
# Copy .env.example to .env and edit docker-compose.yml if required.
|
|
||||||
# In particular, you may want /etc/platypush and /var/lib/platypush
|
|
||||||
# to point to directories on your hosts
|
|
||||||
$ docker compose up
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Note that the default `Dockerfile` uses Alpine, but in `docker-compose.yml` you
|
|
||||||
can also specify an alternative `Dockerfile` - Debian, Ubuntu and Fedora are
|
|
||||||
supported.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Manual installation
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
|
||||||
$ git clone https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush.git
|
|
||||||
$ cd platypush
|
|
||||||
$ pip install .
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Plugins installation
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
All the plugins included in the main repo will be available once you have
|
|
||||||
installed the core platform.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
However, some plugins may require extra (optional) dependencies. You have
|
|
||||||
several ways of installing those dependencies:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### `pip`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You can install extra dependencies via pip extras:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
|
||||||
pip install 'platypush[plugin1,plugin2,...]'
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For example:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
|
||||||
pip install 'platypush[light.hue,music.mpd,rss]'
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Will install Platypush with the dependencies for the `light.hue`, `music.mpd`
|
|
||||||
and `rss` plugins.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Web interface
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Plugins can be installed from the Web interface too. Navigate to the
|
|
||||||
_Extensions_ entry in the sidebar, select the extension that you want to install,
|
|
||||||
select the _Install_ tab and click _Install_.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This section also includes the _Configuration_ tab, with a ready-to-paste
|
|
||||||
configuration snippet template for that plugin, as well as a documentation page
|
|
||||||
that includes all the actions supported by a given plugin and the events it
|
|
||||||
triggers.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Docker
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you already have the base installation of Platypush on your machine, and you
|
|
||||||
have a configuration file with a custom set of integrations, then you may opt
|
|
||||||
to generate a custom Docker image from your configuration file, with all the
|
|
||||||
extra dependencies configured, using the `platydock` command.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The following command:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```shell
|
|
||||||
❯ platydock -c /path/to/your/config.yaml -d platypush-test
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Will create a Platypush Docker image for a device with ID `platypush-test`,
|
|
||||||
with all the requirements for the additional integrations listed in
|
|
||||||
`config.yaml`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You can pass the `--print` option if you just want to print the content of the
|
|
||||||
output `Dockerfile` instead of generating the image.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
By default the image will use Alpine Linux as a base. You can use the
|
|
||||||
`-i`/`--image` to specify another supported base image - `ubuntu`, `debian` or
|
|
||||||
`fedora`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Virtual environment
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you already have the base installation of Platypush on your machine, and you
|
|
||||||
have a configuration file with a custom set of integrations, then you may opt
|
|
||||||
to generate a custom virtual environment from your configuration file, with all
|
|
||||||
the extra dependencies configured, using the `platyvenv` command.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The following command:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
|
||||||
❯ platyvenv -c /path/to/your/config.yaml -o /path/to/your/venv
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Will create a new virtual environment under `/path/to/your/venv` using the
|
|
||||||
specified `config.yaml` to determine which optional dependencies should be installed.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You can then run Platypush after activating your new environment:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
|
||||||
❯ source /path/to/your/venv/bin/activate
|
|
||||||
❯ platypush -c /path/to/your/config.yaml
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Manual installation
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The [plugin/backend documentation](https://docs.platypush.tech) reports all the
|
|
||||||
dependencies required by each plugin, as well as the commands to install them
|
|
||||||
on multiple platforms.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you want to customize your installation, or if you need to install
|
|
||||||
dependencies for a plugin that requires some manual steps, you can check out
|
|
||||||
any plugin-specific installation steps from its documentation.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Configuration
|
## Configuration
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Configuration file
|
### Configuration file
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue